Cloud Computing Service: In today’s fast-paced digital landscape, understanding the dynamics of cloud computing services is not just beneficial; it’s imperative. So, let’s dive straight into the core of this transformative technology.
READ ALSO:
- Cloud Servers: The Power for Business Growth
- What Companies are in the Consumer Services Field
- The Principles of Corporate Finance
- Exploring the World of Insurance Buyouts
Demystifying Cloud Computing Services
Defining Cloud Computing: Decoding the Basics
Cloud computing, in essence, is a revolutionary technology that enables users to access and utilize a pool of computing resources over the internet. From storage to processing power, the cloud offers a flexible and scalable solution to meet diverse business needs.
Key Components of Cloud Services
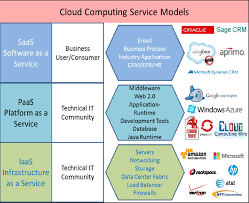
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
IaaS provides the foundational elements, such as virtual machines and storage, allowing businesses to build and manage their IT infrastructure without the hassle of physical hardware.
Platform as a Service (PaaS)
PaaS takes it a step further by offering a platform that includes tools and services for application development, making the entire process more efficient and streamlined.
Software as a Service (SaaS)
SaaS delivers ready-to-use software applications over the internet, eliminating the need for installation and maintenance on individual devices.
The Advantages: Why Businesses are Embracing Cloud Services
Scalability and Flexibility
One of the primary benefits of cloud computing is its ability to scale resources based on demand. Businesses can effortlessly adapt to changing workloads without the constraints of traditional infrastructure.
Cost-Efficiency
Cloud services follow a pay-as-you-go model, allowing businesses to optimize costs by only paying for the resources they use. This eliminates the need for large upfront investments in hardware and infrastructure.
Enhanced Collaboration and Accessibility
The cloud facilitates seamless collaboration among team members, regardless of their geographical location. With data accessible from any device with an internet connection, collaboration becomes a breeze.
Overcoming Concerns: Security and Reliability
Security Measures in Cloud Computing
Cloud service providers invest heavily in security protocols to ensure the protection of sensitive data. From encryption to multi-factor authentication, robust measures are in place to safeguard information.
Reliability through Redundancy
Cloud services operate on redundant systems, minimizing the risk of downtime. Even in the rare event of a server failure, data remains accessible through backup servers, ensuring continuous operations.
Embracing the Future: Evolving Trends in Cloud Computing
Edge Computing
Edge computing, an emerging trend, involves processing data closer to its source rather than relying solely on centralized cloud servers. This reduces latency and enhances real-time processing capabilities.
AI and Machine Learning Integration
The integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning within cloud services is reshaping how businesses analyze and utilize data, providing valuable insights for informed decision-making.
Navigating Cloud Service Models
Public Cloud Services
Public cloud services are accessible to the general public, with resources shared among multiple users. This cost-effective model is suitable for businesses of all sizes, providing on-demand scalability.
Private Cloud Solutions
Private clouds, on the other hand, offer dedicated resources for a single organization. This model ensures enhanced control over data and security, making it ideal for businesses with specific compliance requirements.
Hybrid Cloud Environments
For those seeking a middle ground, hybrid clouds combine elements of both public and private models. This flexibility allows businesses to optimize performance while addressing unique operational needs.
Ensuring a Seamless Transition: Cloud Migration Strategies
Assessment and Planning
Before embarking on a cloud migration journey, a comprehensive assessment of existing systems and a detailed migration plan are crucial. This ensures a smooth transition with minimal disruptions.
Data Migration Best Practices
Effective data migration involves careful planning to avoid potential pitfalls. Encryption, data validation, and regular backups play pivotal roles in safeguarding data integrity during the migration process.
Industry-Specific Applications: Tailoring Cloud Services to Your Needs
Healthcare
In the healthcare sector, cloud computing enhances collaboration among medical professionals, facilitates secure data storage, and supports advanced analytics for better patient care.
E-commerce
For e-commerce businesses, the scalability of cloud services ensures seamless handling of varying workloads, especially during peak shopping seasons. This results in improved user experiences and increased customer satisfaction.
The SEO Advantage of Cloud Computing
Page Loading Speed and SEO Rankings
Search engines prioritize fast-loading websites, and cloud computing significantly contributes to improved page loading speeds. This can positively impact SEO rankings, leading to better visibility online.
Mobile Optimization and User Experience
With the increasing use of mobile devices, cloud services enable businesses to optimize their websites for mobile users. This not only enhances the user experience but also aligns with search engine algorithms favoring mobile-friendly sites.
To know more click here to learn the benefits and types.
Embracing Innovation: Cloud-Native Technologies
Serverless Computing
Serverless computing allows businesses to focus solely on their code, eliminating the need to manage server infrastructure. This results in increased agility and reduced operational overhead.
Containerization and Microservices
Containerization and microservices architecture enhance application development and deployment, providing a more modular and scalable approach. This fosters innovation by enabling continuous delivery and integration.
Staying Ahead with Cloud Security Measures
Encryption Protocols
Security remains a paramount concern in the digital landscape. Cloud computing addresses this with robust encryption protocols, ensuring that data transmitted and stored in the cloud remains confidential and secure.
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
Implementing MFA adds an extra layer of security by requiring users to provide multiple forms of identification before accessing sensitive data. This significantly reduces the risk of unauthorized access.
Real-world Applications: Success Stories in Cloud Integration
Netflix: A Streaming Giant in the Cloud
Netflix relies on cloud computing to deliver seamless streaming experiences to millions of users globally. The scalability of the cloud ensures that the platform can handle peak demand without compromising performance.
Salesforce: Cloud-Powered Customer Relationship Management
Salesforce revolutionized customer relationship management by leveraging cloud technology. This allows businesses to access, manage, and analyze customer data efficiently, fostering stronger client relationships.
Future Trends: Anticipating the Next Frontier in Cloud Computing
Quantum Computing Integration
As technology advances, the integration of quantum computing into cloud services is on the horizon. This revolutionary shift promises unparalleled processing speeds, opening new possibilities for data-intensive applications.
Edge AI and Cloud Synergy
Combining edge AI with cloud computing enhances the capabilities of both technologies. The edge handles real-time processing, while the cloud manages complex computations, offering a synergistic solution for diverse applications.
Navigating Cloud Service Providers: Making Informed Choices
Amazon Web Services (AWS)
AWS, a frontrunner in the cloud industry, provides a comprehensive suite of services, from computing power to database management. Its global infrastructure ensures reliable and scalable solutions.
Microsoft Azure: A Holistic Cloud Ecosystem
Microsoft Azure offers a diverse range of cloud services, including AI and machine learning capabilities. Its seamless integration with Microsoft products makes it a preferred choice for businesses using Microsoft solutions.
Google Cloud Platform (GCP)
Known for its data analytics and machine learning offerings, GCP provides a robust infrastructure for businesses seeking innovative solutions. Its global network ensures low-latency access to services.
Ensuring a Smooth Transition: Best Practices for Cloud Adoption
Employee Training and Change Management
Successful cloud adoption requires a workforce equipped with the necessary skills. Investing in employee training ensures a seamless transition and maximizes the potential of cloud technologies.
Continuous Monitoring and Optimization
Once migrated to the cloud, continuous monitoring is vital to identify potential bottlenecks and optimize resource usage. This proactive approach enhances efficiency and reduces operational costs.
Eco-friendly Cloud Computing: A Sustainable Advantage
Energy Efficiency in Cloud Data Centers
Major cloud service providers prioritize sustainability by designing energy-efficient data centers. This not only reduces the environmental impact but also aligns with corporate social responsibility goals.
Reducing E-waste through Cloud Services
Cloud computing minimizes the need for physical hardware, decreasing electronic waste. This eco-friendly aspect is increasingly becoming a crucial consideration for businesses committed to sustainability.
Cloud Computing in a Post-Pandemic Landscape
Remote Work Enablement
The COVID-19 pandemic accelerated the shift towards remote work, underscoring the importance of cloud computing. Cloud services enable seamless collaboration and access to critical resources from anywhere in the world.
Business Continuity and Disaster Recovery
Cloud-based solutions provide robust business continuity and disaster recovery mechanisms. In times of unforeseen disruptions, data remains accessible, ensuring minimal downtime and a quick recovery.
Crafting a Competitive Edge: Cloud Services and Small Businesses
Affordability and Scalability for Small Businesses
Cloud computing levels the playing field for small businesses, offering affordable solutions with the flexibility to scale as operations expand. This strategic advantage enhances competitiveness in the market.
Access to Advanced Technologies
Small businesses gain access to cutting-edge technologies through cloud services, such as AI and analytics, without the need for substantial upfront investments. This fosters innovation and growth.
The Human Touch in Cloud Computing: Customer Support and Service Excellence
Customer Support in the Cloud Industry
When selecting a cloud service provider, the quality of customer support is paramount. Providers offering responsive and reliable customer service contribute to a positive experience for businesses relying on their services.
Service-Level Agreements (SLAs) and Accountability
Clear and comprehensive SLAs establish expectations between businesses and cloud service providers. Ensuring accountability and transparency in service delivery is vital for maintaining a strong client-provider relationship.
Final Thoughts: Embracing the Future of Computing
In conclusion, the era of cloud computing is a transformative journey that transcends technological advancements. It’s a paradigm shift that reshapes the way businesses operate, innovate, and connect with the world.
As you embark on or enhance your cloud computing journey, consider the holistic impact on your organization. From environmental sustainability to empowering a remote workforce, the cloud is a catalyst for positive change and enduring success.
cloud computing service
cloud computing service
cloud computing service
cloud computing service